Manually Deploy Appchain Node
# Manually Deploy Appchain Node
Note
Before manually running an Appchain node, make sure you can handle node issues and exceptions. If there is a problem with the node, both the validator and its delegators will not be able to receive restaking rewards.
Learn how to run an Appchain node. To manually deploy the Appchain node, the validator can choose their favorite VPS provider, and generally using the Ubuntu operating system.
Note
Make sure your server has installed Go and necessary libraries which would be used to build Appchain node binary.
- Install Go (opens new window)
- Install libraries:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade -y && sudo apt-get install -y curl make git libc-dev bash gcc jq
The following steps are required:
- Build Appchain node binary
- Initialize Node
- Config Node
- Run the Appchain Node
# Build Appchain node binary
Click the Appchains and select the appchain which would like to be a validator, click it to open the appchain page, you can get the GitHub repo and Chain ID of Appchain.
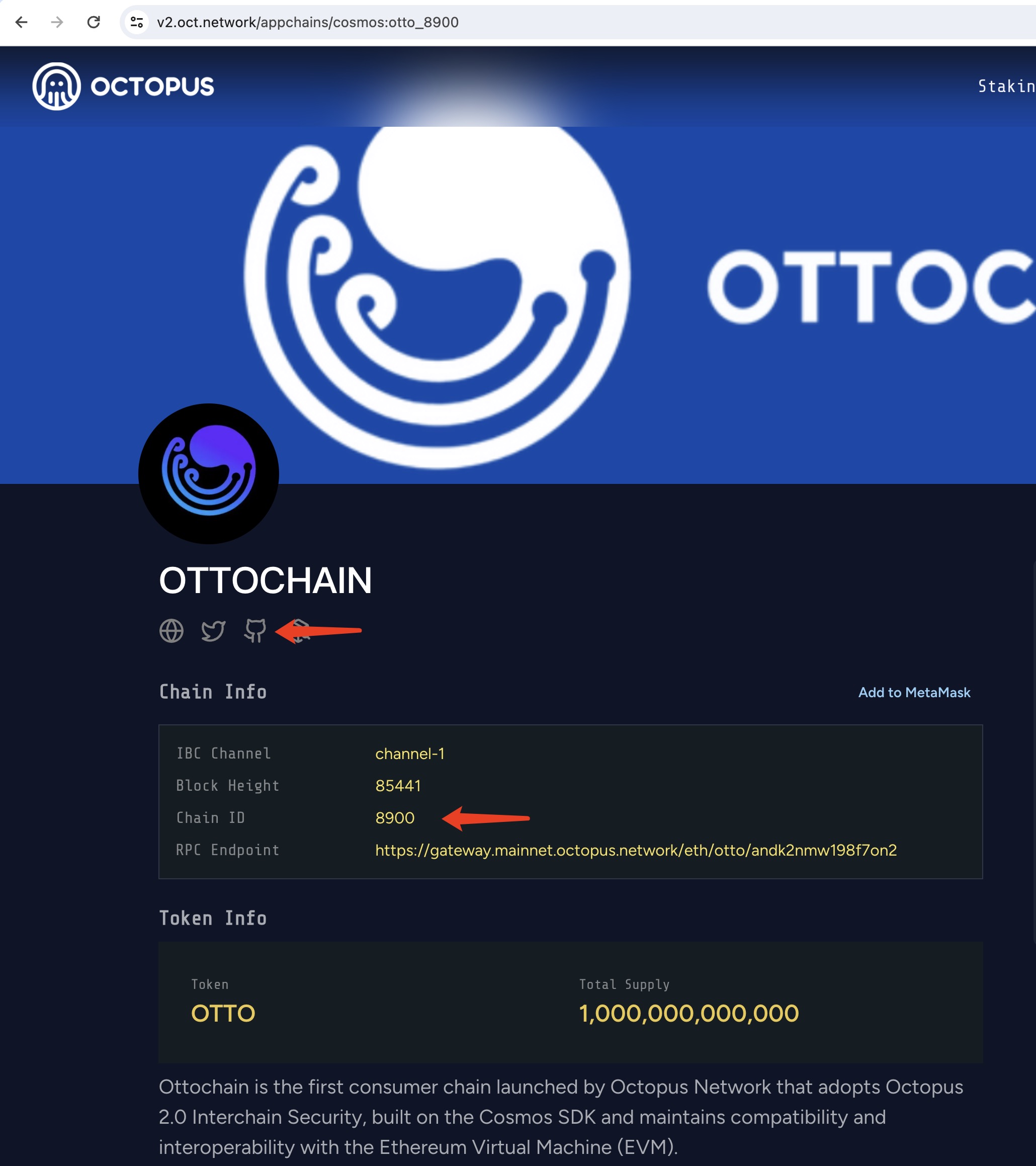
An example of building the Ottochain node binary is as follows:
git clone https://github.com/ottochain/otto.git
cd otto
make install
ottod -h
If you get the error ottod: command not found, please run the go env to check your GOPATH, and then run cp $GOPATH/bin/ottod /usr/local/go/bin/ottod. Now ottod -h should work fine.
# Initialize Node
Run the following command to initialize the node to create all the necessary validator and node configuration files:
<appchain_binary> init <your_custom_moniker> --chain-id <appchain_chain_id>
By default, the init command creates your ~/.<appchain_binary> directory with subfolders config/ and data/. In the config directory, the most important files for configuration are app.toml and config.toml.
~/.<appchain_binary>
├── config
│ ├── app.toml # Application-related configuration file.
│ ├── client.toml
│ ├── config.toml # Tendermint-related configuration file.
│ ├── genesis.json # The genesis file.
│ ├── node_key.json # Private key to use for node authentication in the p2p protocol.
│ └── priv_validator_key.json # Private key to use as a validator in the consensus protocol.
└── data # Contains the databases used by the node.
└── priv_validator_state.json
You can easily change the default directory by using the --home flag.
An example of using OttoChain ottod is as follows:
ottod init my-validator --chain-id otto_8900-1
# Get the validator pubkey
Validator need to get the validator pubkey (only for the validator who manually deploy Appchain node), which used to set it to the Appchain node. You can get your validator pubkey on your validator node by running show-validator command.
An example of using OttoChain ottod is as follows:
ottod tendermint show-validator
{"@type":"/cosmos.crypto.ed25519.PubKey","key":"2CKdA3Sbl1hh6+Exdqy7LfspfGcgUtNhV1VwUAZcy7c="}
You need to save the value of key(e.g.2CKdA3Sbl1hh6+Exdqy7LfspfGcgUtNhV1VwUAZcy7c=) for the next step - bond validator.
# Config Node
You can get appchain configuration from the GitHub repo of Appchain and then config your node.
For example:
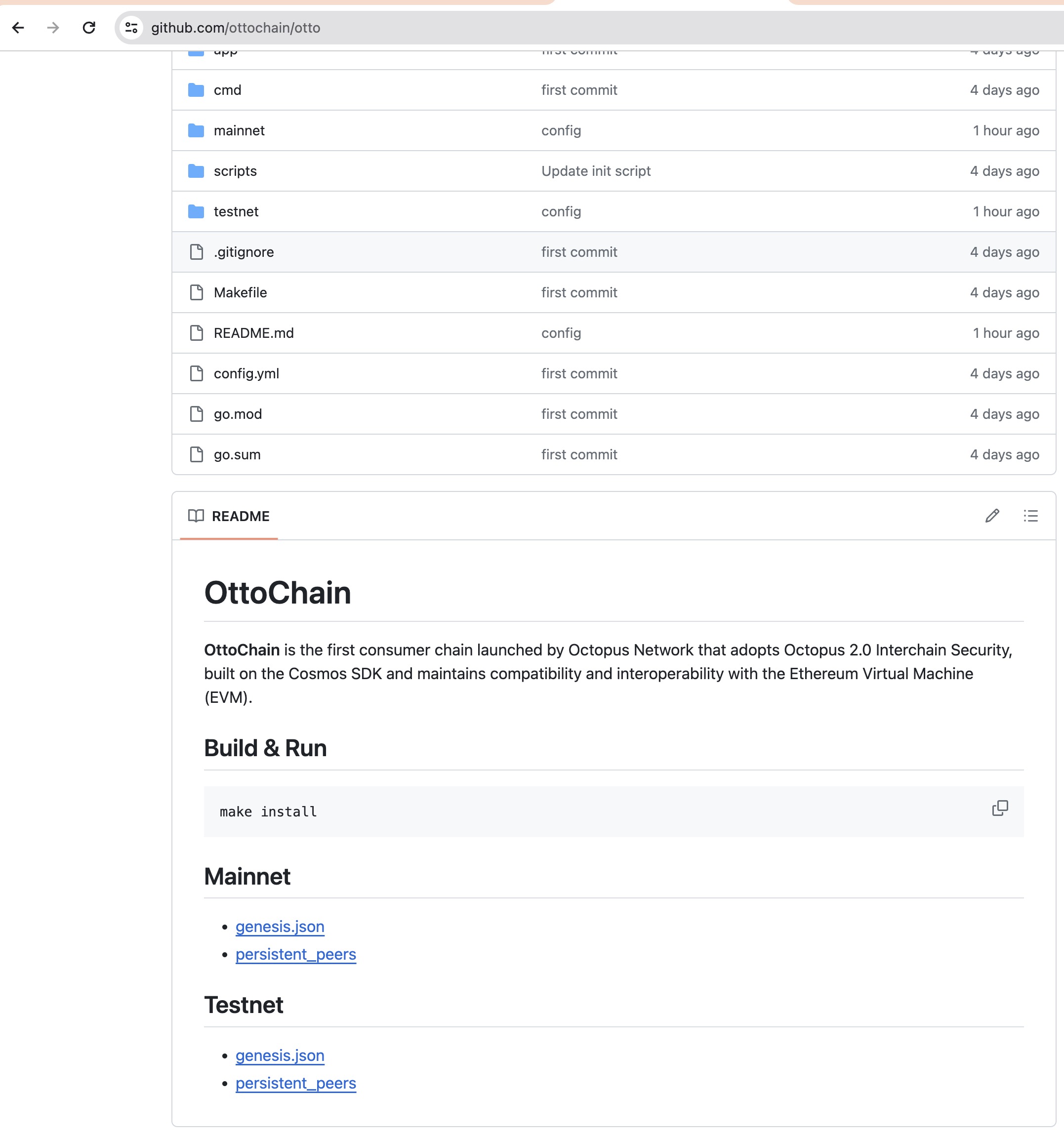
# Copy the Genesis File
Download the genesis.json file from the appchain repo and copy it over to the config directory (e.g. ~/.<appchain_binary>/config).
An example of using OttoChain ottod is as follows:
wget -O ~/.ottod/config/genesis.json https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ottochain/otto/main/mainnet/genesis.json
# Add Persistent Peers
Your validator node needs to connect peers (opens new window) and maintain persistent connections with them. You'll need to set the persistent_peers field in config.toml under the config directory (e.g. ~/.<appchain_binary>/config) with the list of available peers on the appchain repo.
Edit the file config.toml and add the persistent peers to the following:
#######################################################
### P2P Configuration Options ###
#######################################################
[p2p]
# ...
# Comma separated list of nodes to keep persistent connections to
persistent_peers = ""
You can also use sed to include them into the configuration. An example of using OttoChain ottod is as follows:
export persistent_peers="38b8a6277c277e63a7bcace0f8d3c0bce3d3fd1b@157.230.120.27:26656,c5373de49272255b85d1f1f55c42851de2d61a81@146.190.99.126:26656,146e4ff134270d8a641b0028445db42fee53e51a@34.71.98.174:26656,47f6ca01467e753208e170f053761fb99549de72@34.42.214.220:26656"
sed -i.bak "s/persistent_peers = \"\"/persistent_peers = \"${persistent_peers}\"/" ~/.ottod/config/config.toml
# Set minimum-gas-prices
You can use sed to change the minimum-gas-prices in the file app.toml.
An example of using OttoChain ottod is as follows:
export IBC_TOKEN_DENOM=`jq -r '.app_state.crisis.constant_fee.denom' ~/.ottod/config/genesis.json`
sed -i.bak "s#minimum-gas-prices = \"0aotto\"#minimum-gas-prices = \"20000000000${IBC_TOKEN_DENOM}\"#" ~/.ottod/config/app.toml
# Run the Appchain Node
Run the following command to start the appchain node in background:
nohup <appchain_binary> start &
An example of using OttoChain ottod is as follows:
nohup ottod start &
And to check the log run the following command:
tail -f nohup.out
6:23AM INF Unlocking keyring module=server
6:23AM INF starting ABCI with Tendermint module=server
6:23AM INF starting node with ABCI Tendermint in-process module=server
6:23AM INF InitChain chainID=otto_8900-1 initialHeight=1 module=server
...
6:23AM INF This node is a validator addr=76CBD1E7565B06A74811C2F592689A6F487B7D38 module=consensus pubKey=2CKdA3Sbl1hh6+Exdqy7LfspfGcgUtNhV1VwUAZcy7c= server=node
6:23AM INF P2P Node ID ID=e25881e99f8a79028b7949bad1de4536802d74e0 file=/root/.ottod/config/node_key.json module=p2p server=node
6:23AM INF Add our address to book addr={"id":"e25881e99f8a79028b7949bad1de4536802d74e0","ip":"0.0.0.0","port":26656} book=/root/.ottod/config/addrbook.json module=p2p server=node
...
6:23AM INF service start impl=baseWAL module=consensus msg={} server=node wal=/root/.ottod/data/cs.wal/wal
6:23AM INF service start impl=Group module=consensus msg={} server=node wal=/root/.ottod/data/cs.wal/wal
...
6:23AM INF commit synced commit=436F6D6D697449447B5B323220353420313535203134322032343920313220313839203331203533203234382031333320383420313234203233382031373920323520302032313220323231203139352032313220373120313933203420323136203232352032302031393820353320313335203130322036325D3A327D module=server
6:23AM INF committed state app_hash=16369B8EF90CBD1F35F885547CEEB31900D4DDC3D447C104D8E114C63587663E height=2 module=state num_txs=0 server=node
6:23AM INF indexed block exents height=2 module=txindex server=node
After the node synchronization, the validator needs to bond validator.
